If you want to know which city has the fastest internet connection in the U.S., you will be surprised to know it is not Silicon Valley. You need to pack your bags and move your business to Chattanooga, Tennessee, where the internet speed is 1 Gigabyte-per-second, available to every home and business – over 150,000 of them. The people of Chattanooga own the electric company EPB which was tasked to install the 100% fiber network paid for by a 320 million dollar bond and line of credit and a 111 million dollar government loan, building the first Smart Grid in the U.S. in 2008, capable of uploading and downloading information 200 times faster than the U.S. national average and 10 times faster than the FCC National Broadband Plan. To give you a sense of the meaning of 1 Gigabyte of internet speed, let me tell you that at the rate of my current internet speed (50 megabytes per second; I live in Maryland) it will take 54 seconds to download 100 pictures compared to 3 seconds for the same amount of pictures using 1 Gigabyte per second. This speed provides many scientific benefits to many schools. The schools interact live with international labs and super computers. Chattanooga public schools are on the cutting edge of science because of this speed. Although the EPB is not making money yet, it is expected to to reach profit within several years.
The Google fiber project, started in 2012, promises to give you 1 Gigabyte per second as well. So far, Google was able to provide Atlanta, Austin, Charlotte, Kansas City, Nashville, Provo, Raleigh-Durham, Salt Lake City, and San Antonio. If you would like to know if your city is next, log into the Google website. As Google is entering the business of hardware computing, the list of cities is expected to grow to hundreds in the next few years. Google’s futuristic vision of building high speed internet is expected to spread great science and engineering advancements so that many cities are approaching Google and showering them with some logistical advantages.
Another project running between many American cities is called ” Next Century Cities”. The collaborative project introduces one Gigabyte of internet speed, connecting people, businesses, communities with new opportunities. This collaboration, established by 100 cities and towns, forms a nonpartisan, city-to-city collaborative work. The cities give each other help and experience to deal with political, financial, and legal difficulties to facilitate one Gigabyte internet speed.
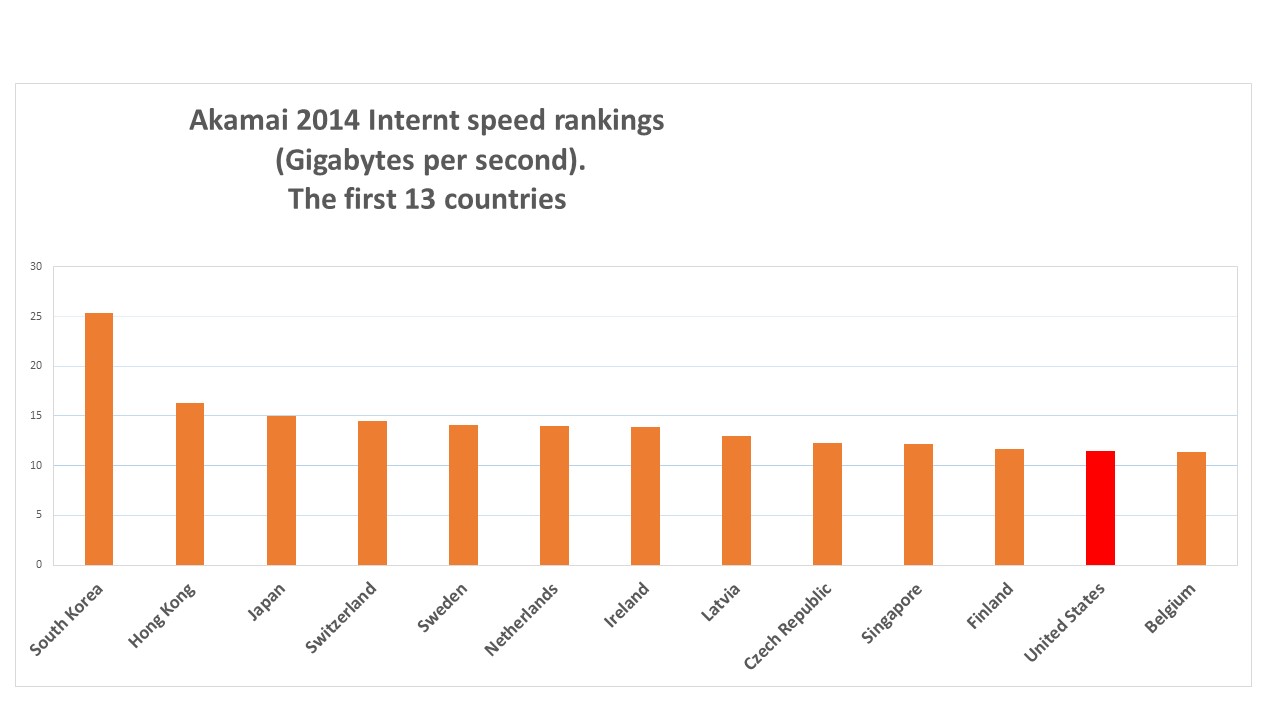
As much as we are happy about this new speed, the United States ranks number 12 in the world in internet speed. Currently the highest speed the internet can reach in the U.S. is 11.5 Gigabyte/sec compared to South Korea 25.3, Hong Kong 16, Japan 15, Switzerland 14.5, Sweden 14.1, Netherlands 14, Latvia 11, Czech Republic 12.3, Singapore 12.2, Finland 11.7, Belgium 11.4 Gigabyte/second.
So how did the United States fall behind in providing high speed internet compared to South Korea?
Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Obama for science, technology, and innovation points out “huge telecommunication companies” such as Comcast, Time Warner, Verizon, and AT&T have “divided up markets and put themselves in a position where they are subject to no competition.” The 1996 Telecommunication Act freed cable companies to divide the U.S. market freely, creating a monopoly by charging customers higher prices without the need to invest in infrastructure – fiber optics. Verizon was the only company that started installing fiber optics but stopped in 2010 after mounting costs. Ms. Crawford discusses several points in this https://player.vimeo.com/video/59236702youtube video.
How did South Korea achieve this success? The South Korean government produced an open access rule to encourage new technologies to advance rather than the incumbent.(Professor Richard Taylor and Eun-A Park via Academic.edu)
As the Google fiber project started scaring the monopoly, telecommunication companies reconsidered their positions. Currently, Comcast offers 2 Gigabytes per second in Chattanooga, Tennessee competing with EPB. The Obama Administration is building publicly-fundedwireless networks to offer fast 4G internet across the U.S.
This blog is usually published every week on Saturday before 10:00 pm. US Eastern time. This post was delayed because of the Thanksgiving holiday- Happy Thanksgiving ! Thank you for reading my blog. I would love to hear from you.